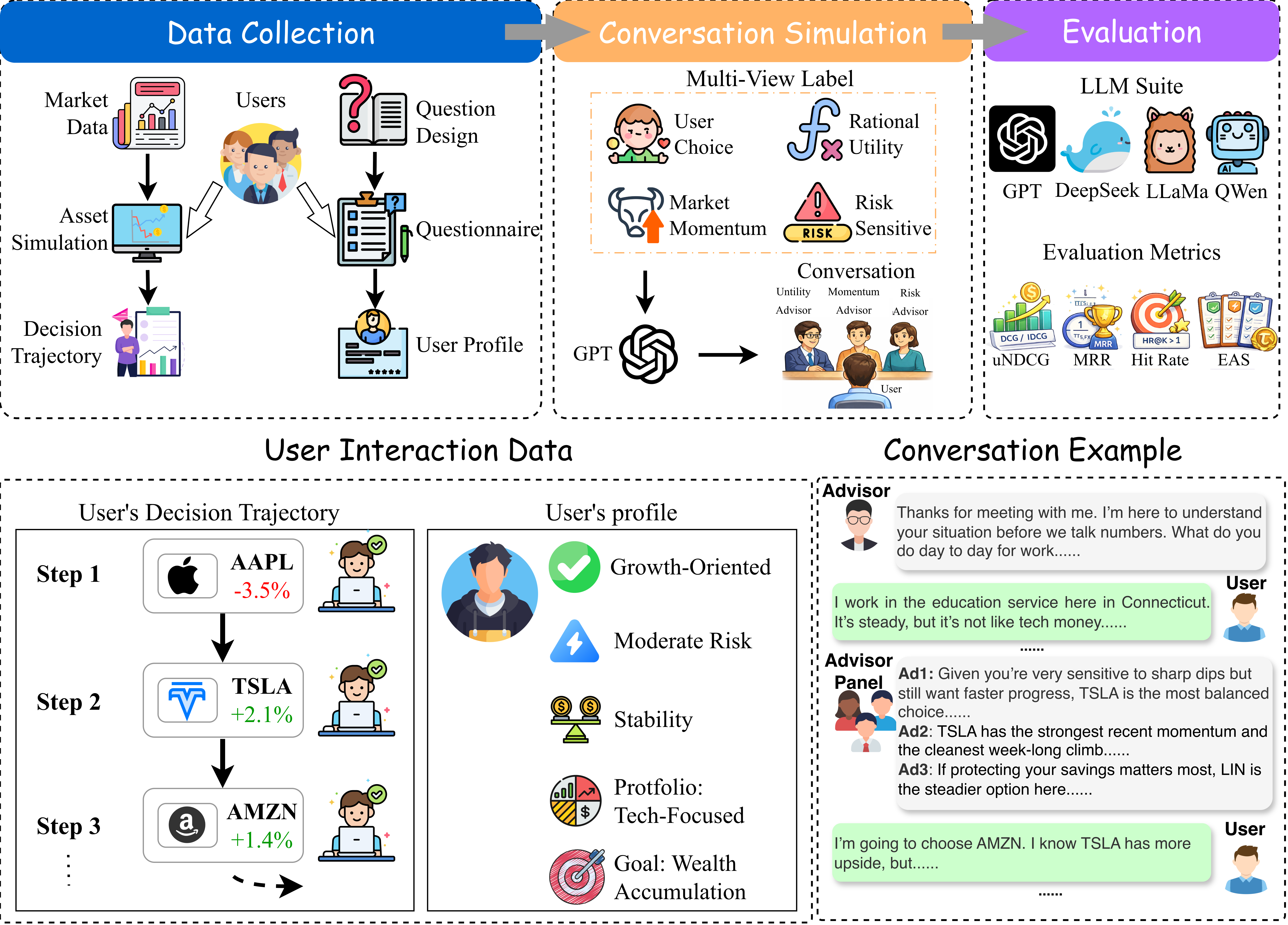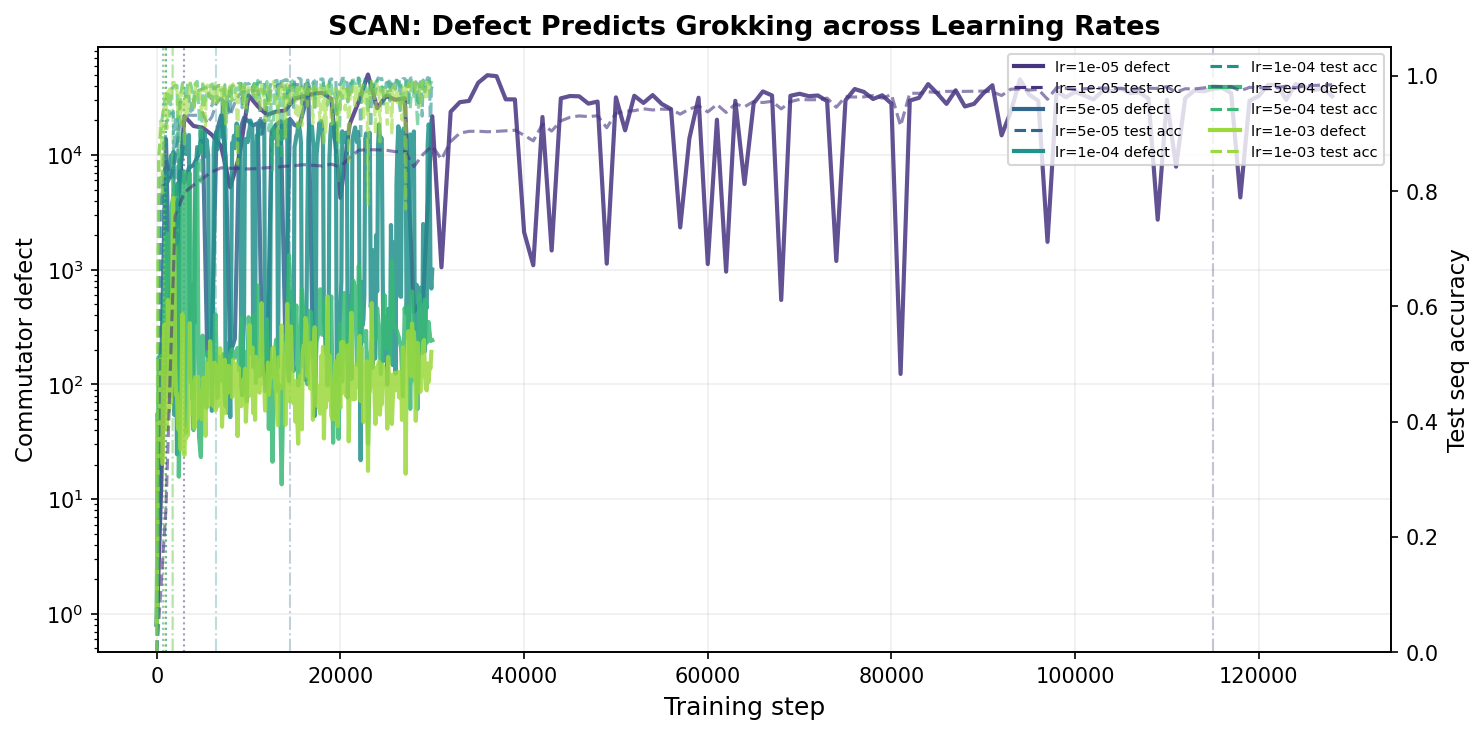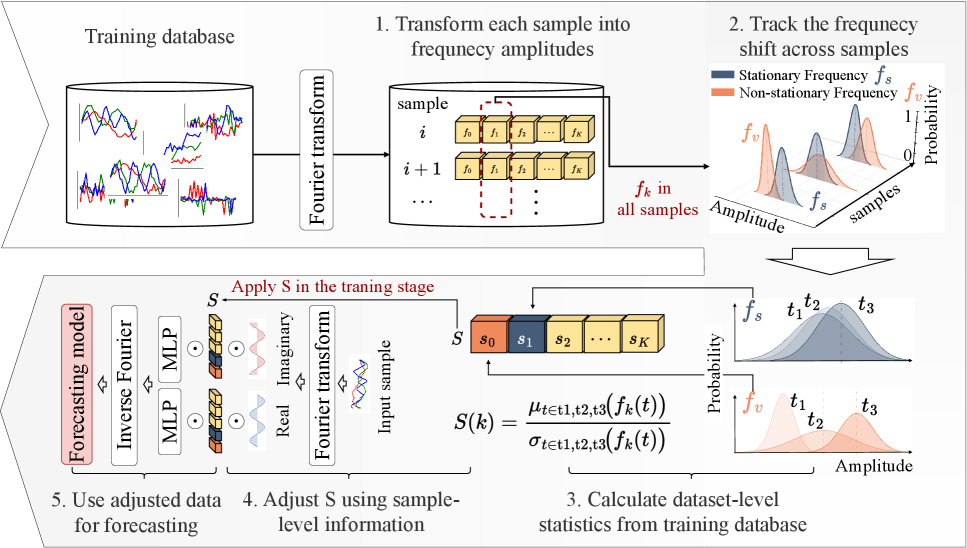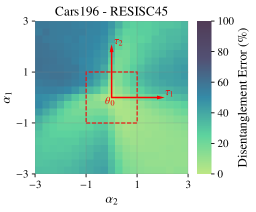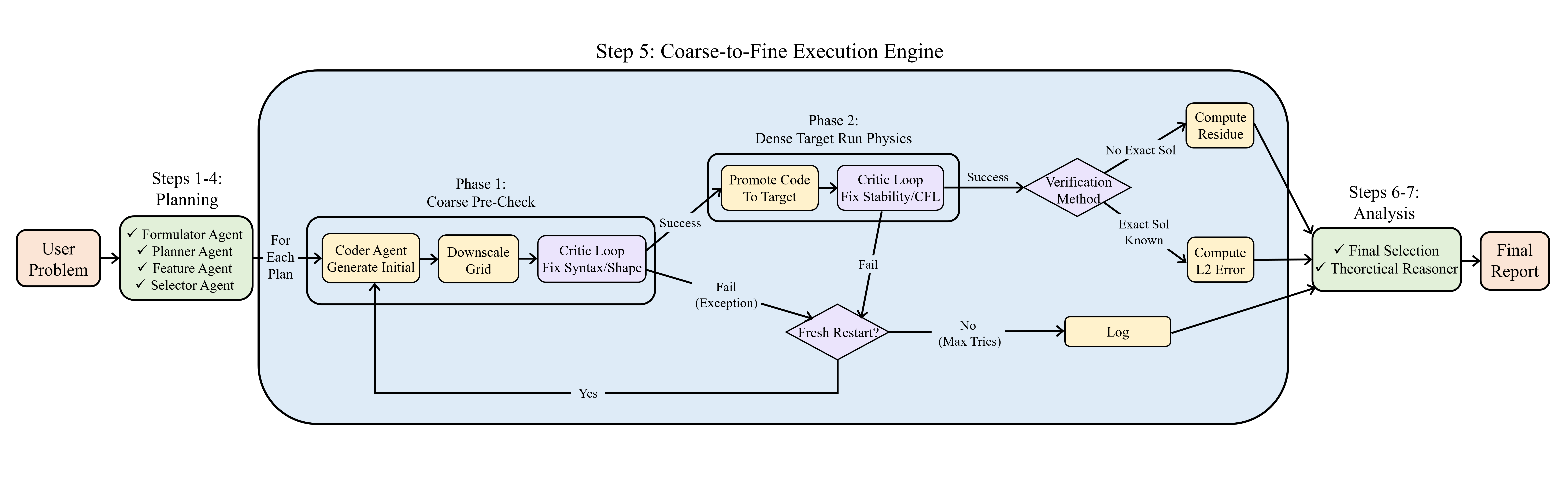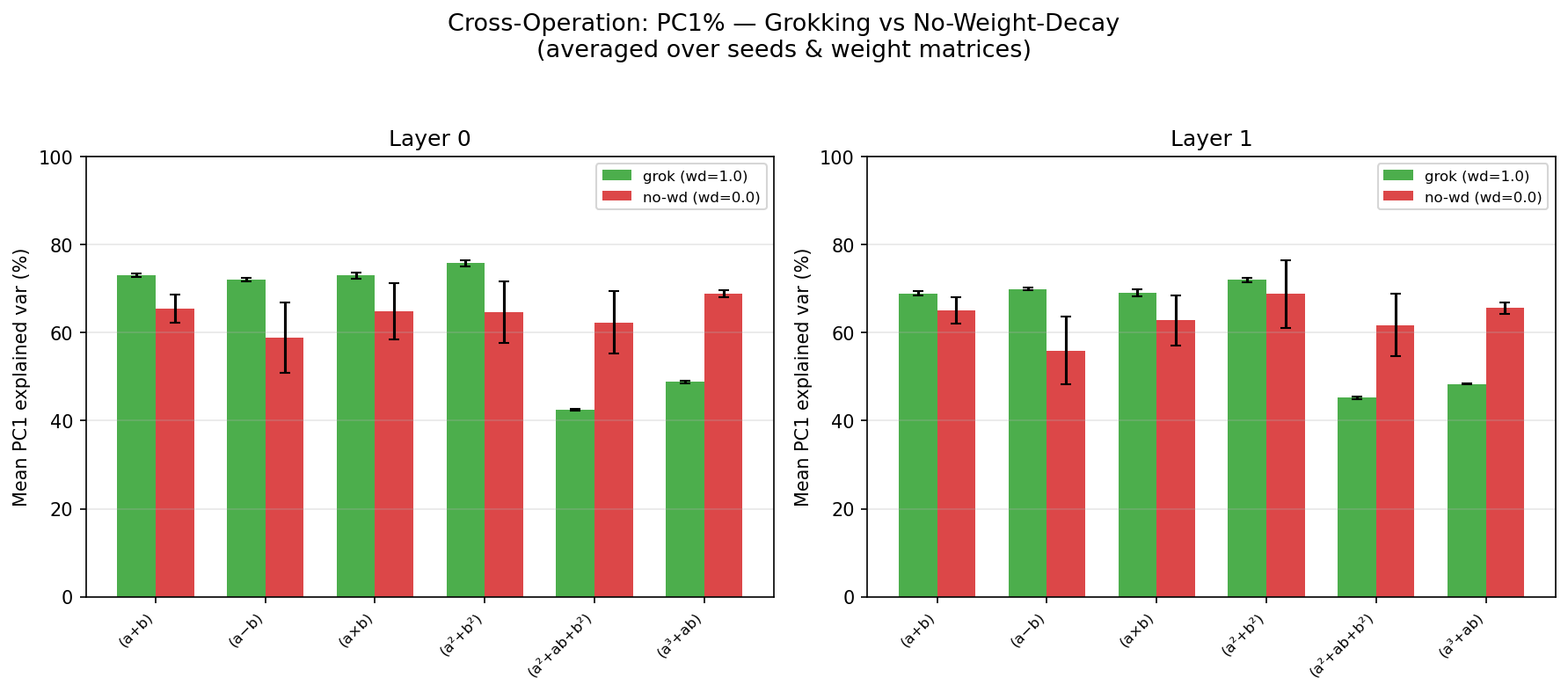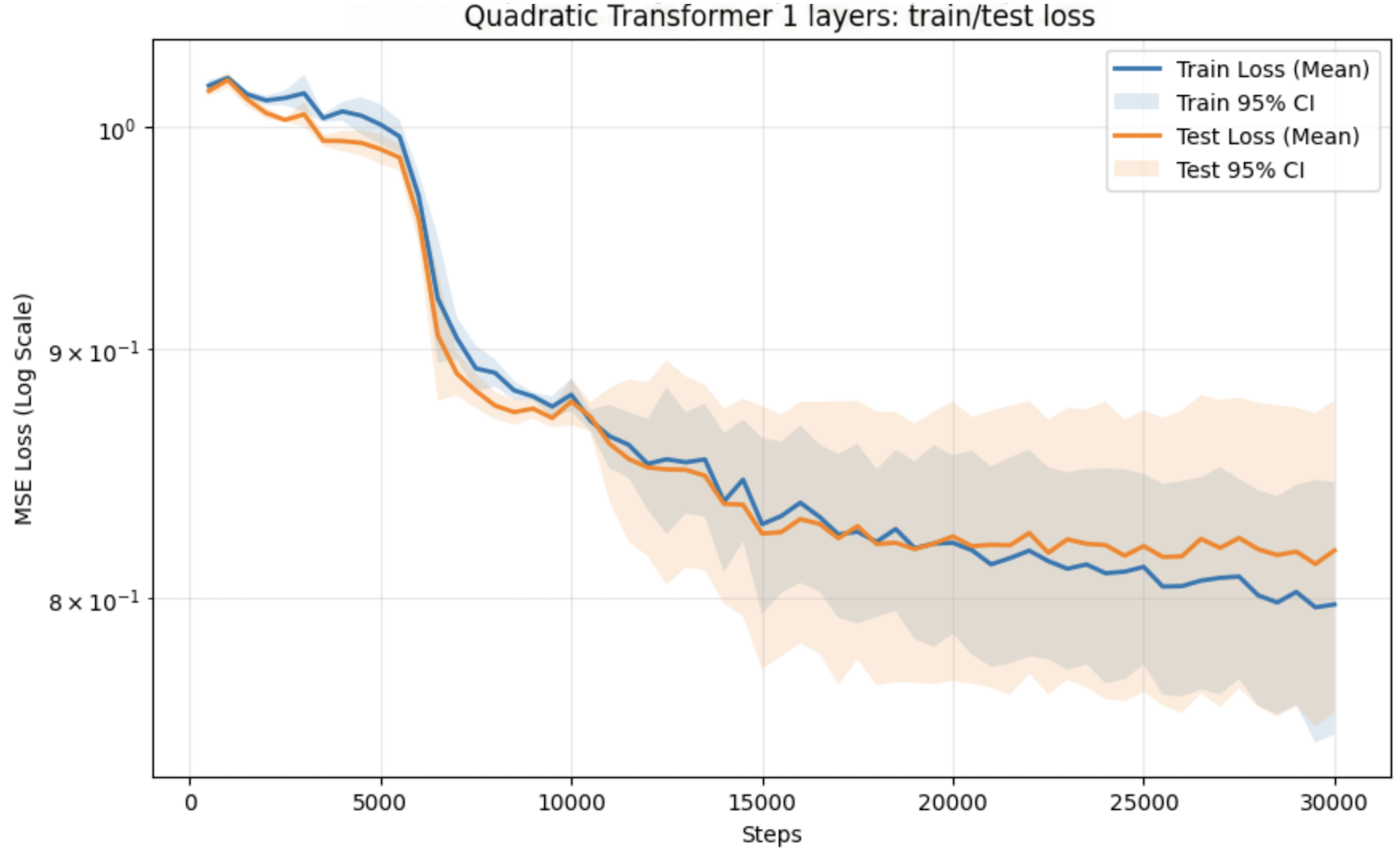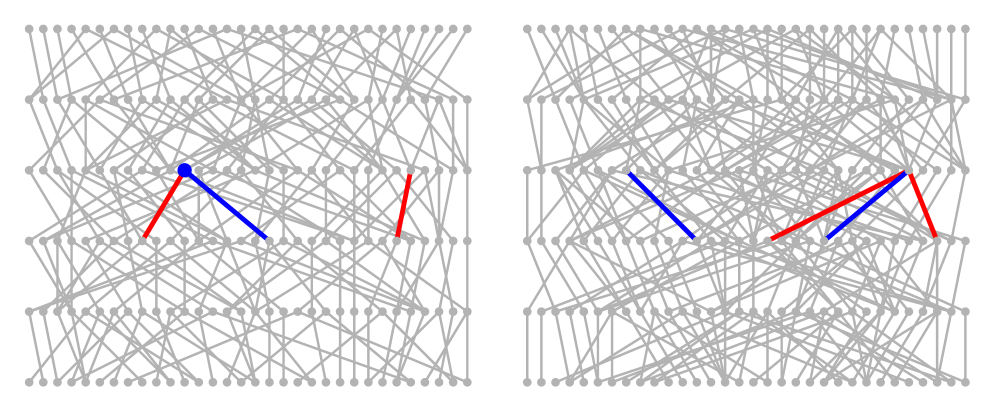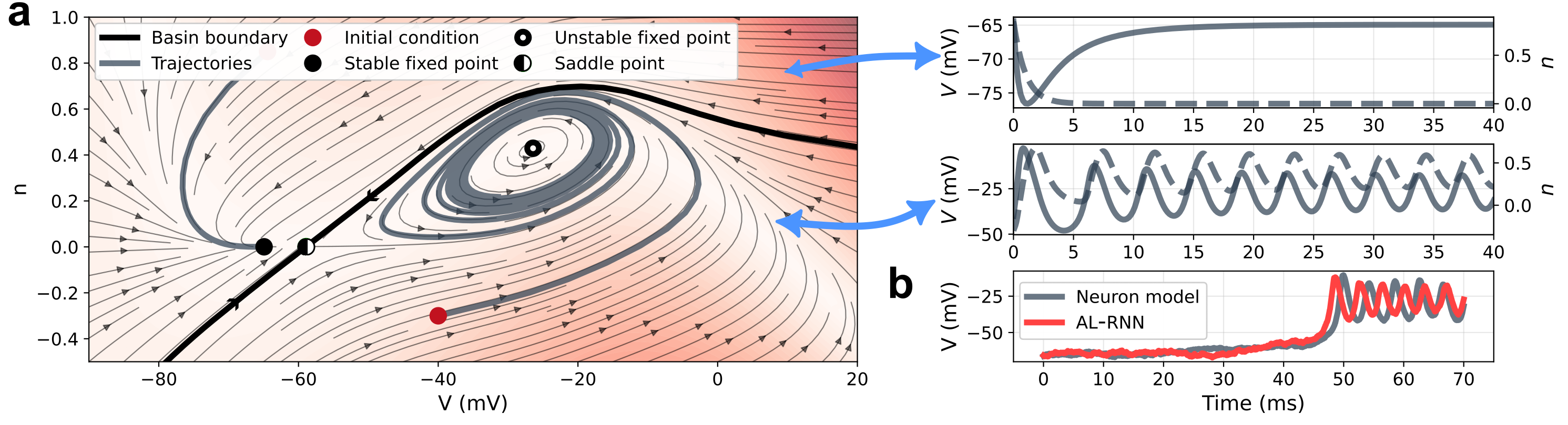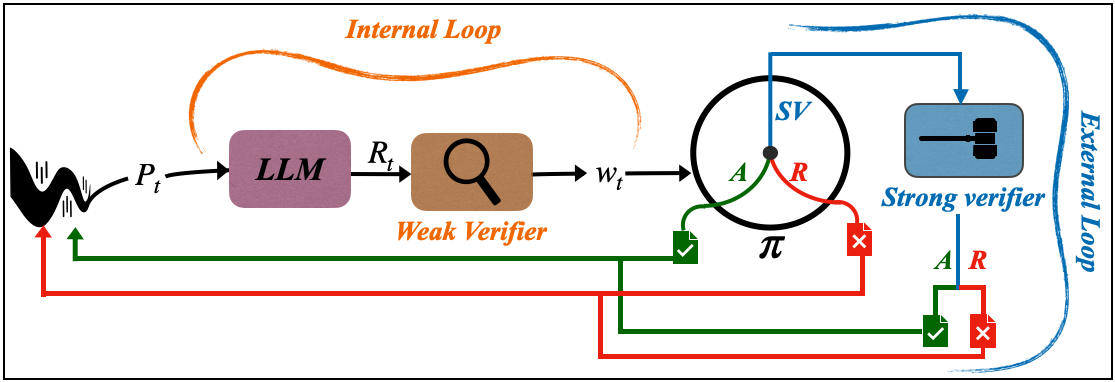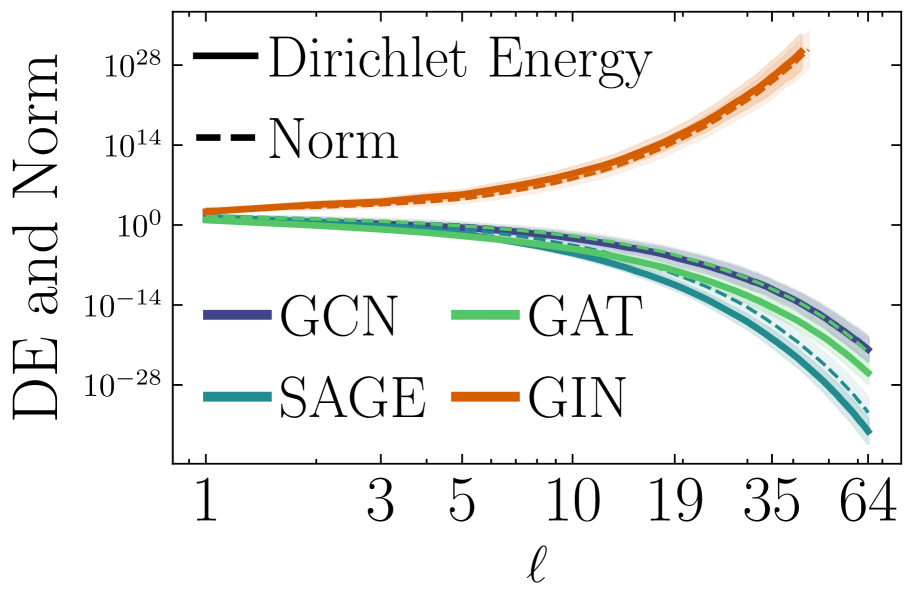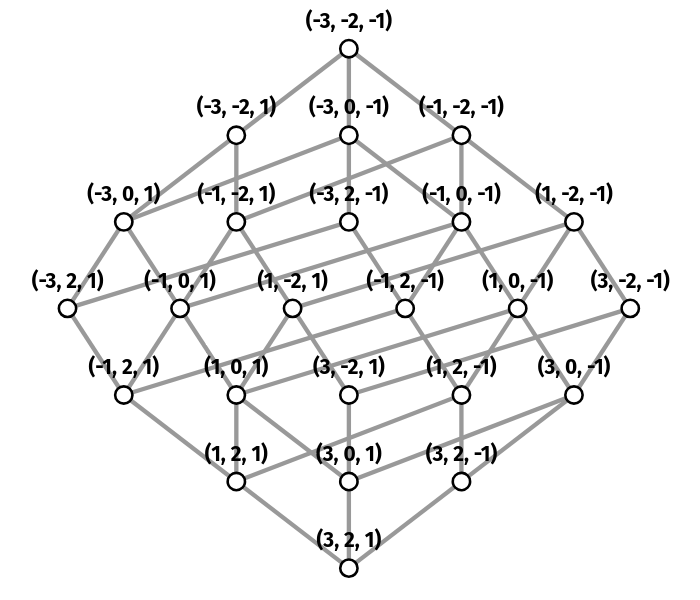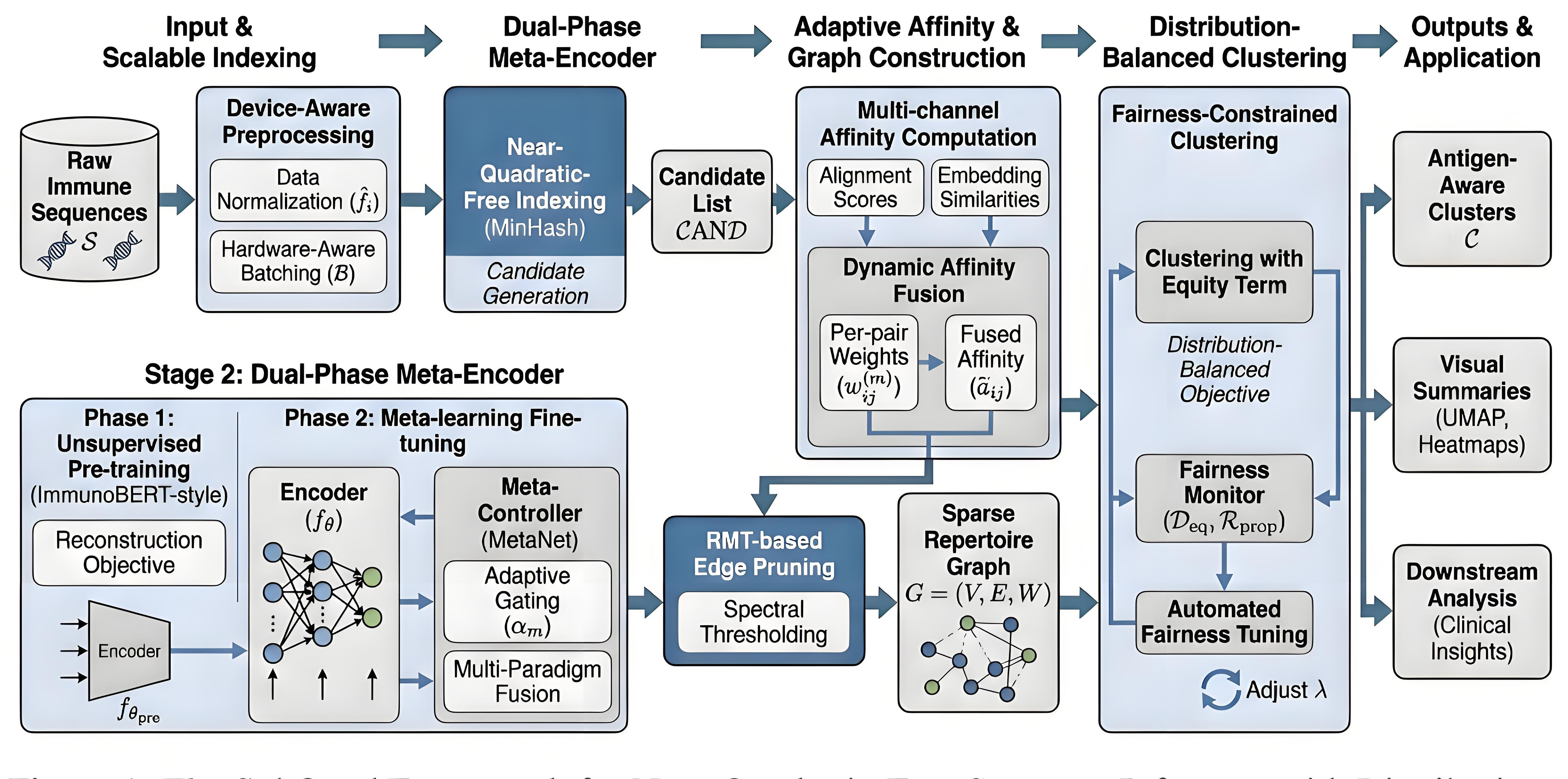
SubQuad: Near-Quadratic-Free Structure Inference with Distribution-Balanced Objectives in Adaptive Receptor framework
A new algorithm can efficiently analyze immune system data to identify rare but important immune cell types, helping doctors understand immune responses and diseases.