Story
VLM-DEWM: Dynamic External World Model for Verifiable and Resilient Vision-Language Planning in Manufacturing
Key takeaway
A new AI system can help robots in factories better understand their surroundings and respond to changes, making manufacturing more reliable and flexible.
Quick Explainer
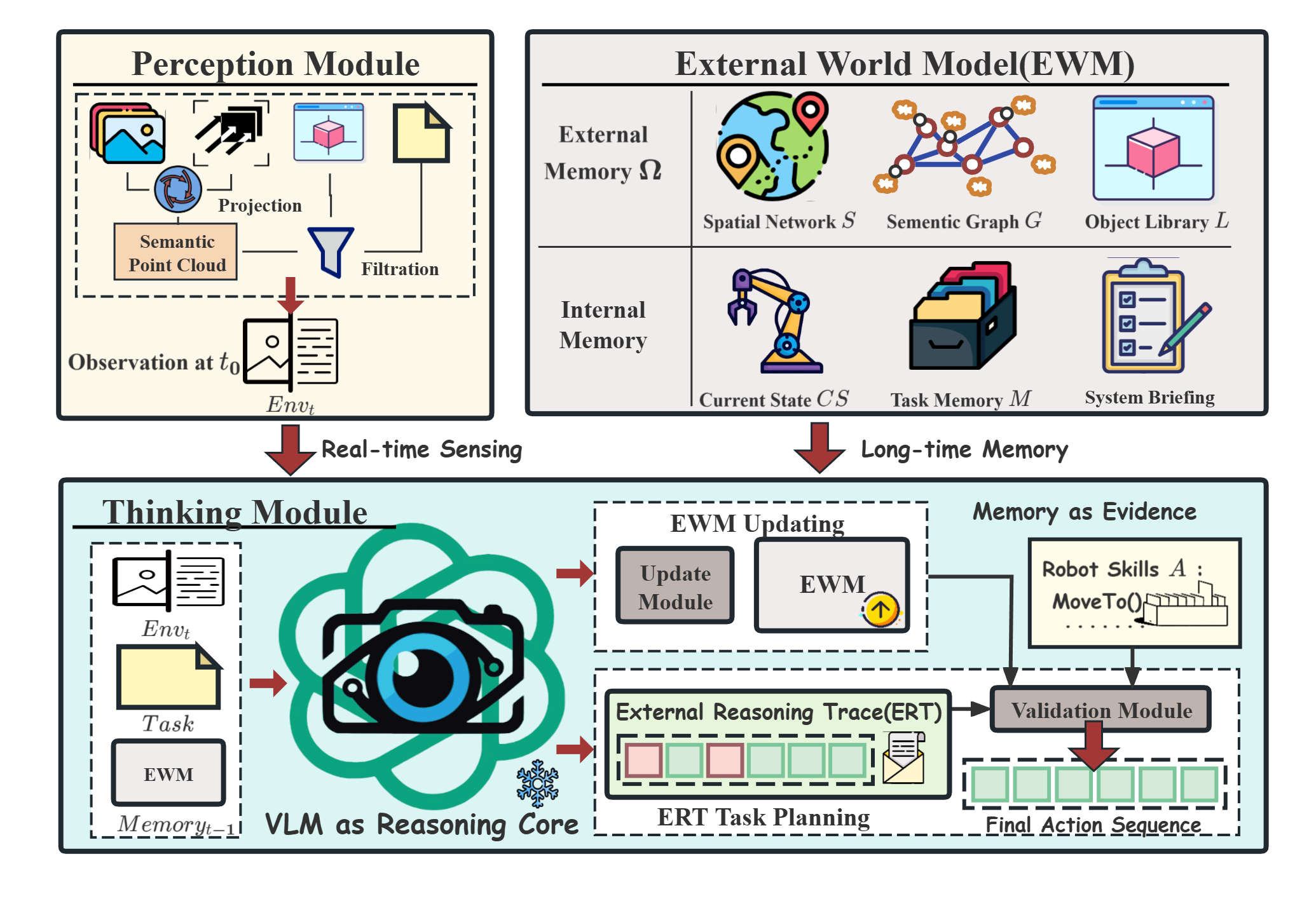
VLM-DEWM is a cognitive architecture that enables robust long-term robotic planning in dynamic environments. It decouples persistent state maintenance from semantic reasoning, addressing two key challenges: state persistence and verifiability. VLM-DEWM maintains a Dynamic External World Model (DEWM) to track object states over time, and structures each decision as an Externalizable Reasoning Trace (ERT) that can be verified against the DEWM before execution. This "Database–Transaction–Verification" approach allows VLM-DEWM to achieve significantly higher reliability, state-tracking accuracy, and recovery success compared to pure VLM-based planners or memory-augmented strategies, as demonstrated across manufacturing-relevant scenarios.
Deep Dive
Technical Deep Dive: VLM-DEWM for Verifiable and Resilient Vision-Language Planning
Overview
This work presents VLM-DEWM, a cognitive architecture for robust long-horizon robotic planning in dynamic manufacturing environments. VLM-DEWM decouples persistent state maintenance from semantic reasoning, addressing two critical challenges in vision-language model (VLM) based planning:
- State Persistence: VLM-DEWM maintains a Dynamic External World Model (DEWM) that tracks object states across occlusions and station transitions, resolving the world-state drift common in pure VLM planners.
- Verifiability and Diagnosability: VLM-DEWM structures each VLM decision into an Externalizable Reasoning Trace (ERT), enabling pre-execution physical consistency checks and precise failure diagnosis when execution fails.
By separating state and reasoning, VLM-DEWM achieves significantly higher reliability, state-tracking accuracy, and recovery success rates compared to state-of-the-art memory-augmented VLM baselines.
Methodology
VLM-DEWM operates on a "Database–Transaction–Verification" paradigm:
- Dynamic External World Model (DEWM): The DEWM maintains a persistent, queryable database of the environment's semantic and geometric state, composed of:
- Spatial Network ($S$): Probabilistic state estimates of object poses and background structures
- Hierarchical Semantic Graph ($G$): Encodes logical relations and affordances
- Shape Prior Library ($L$): High-fidelity geometric models for robust pose estimation
- Externalizable Reasoning Trace (ERT): Each VLM decision is structured into an ERT, containing the proposed action, the VLM's world belief, and its causal assumption. The ERT is verified against the DEWM before execution.
- Validation and Closed-Loop Recovery: A closed-loop cognitive pipeline synthesizes task-specific queries from the DEWM, audits VLM outputs through multi-layer checks, and performs targeted failure diagnosis when discrepancies arise between predicted and observed outcomes.
Experimental Setup
The authors evaluated VLM-DEWM in simulation and on a real-world robotic platform across three manufacturing-relevant scenarios:
- Long-Horizon Multi-Stage Assembly: Requires the robot to complete a 10+ step assembly process while maintaining cross-station state consistency.
- Large-Scale Facility Exploration: Assesses the system's ability to build a comprehensive semantic map and answer spatial reasoning queries about the entire facility.
- Dynamic Exception Handling: Introduces real-world execution failures (gripper slips, unexpected obstacles) and measures the system's ability to diagnose and recover.
VLM-DEWM was compared against two categories of baselines:
- Context-Only VLM Planners: Rely solely on the VLM's context window for state maintenance.
- Memory-Enhanced Strategies: Augment VLMs with external memory structures (e.g., SAGE, GEAR).
Key Results
- Long-Horizon Reliability: VLM-DEWM achieved a 94% task success rate with near-perfect state-tracking accuracy (100%), outperforming pure VLM baselines (0-28% success) and memory-enhanced strategies (0-72% success).
- Precise Diagnosis and Recovery: In the dynamic recovery task, VLM-DEWM achieved a 95% success rate, while all baselines failed completely (0% success). Its ability to precisely diagnose failure causes (36.96% causal diagnosis accuracy) enabled informed replanning, in contrast to the "blind retries" of the baselines.
- Sim-to-Real Generalization: The results on the physical Franka platform closely matched the simulation, demonstrating the system's ability to generalize from privileged information to real-world sensor noise and latency.
Limitations and Uncertainties
- Upstream Perception Errors: VLM-DEWM faithfully memorizes any corrupted inputs from the symbolic perception interface, and cannot self-correct these errors.
- Closed-World Assumption: The system assumes a semi-structured environment where object categories are known. Handling novel, open-vocabulary objects remains a challenge.
- Dynamics Gap: The current physical verification focuses on geometric feasibility, but does not validate dynamics (e.g., payload stability) or kinematics (e.g., joint limits).
- Granularity Limits of Causal Diagnosis: While the system can diagnose high-level topological mismatches, it lacks the physical granularity to pinpoint the exact root cause (e.g., friction vs. force).
- Reactivity Limitations: As a deliberative system, VLM-DEWM incurs a latency cost that may create a "Reactivity Gap" for highly dynamic tasks requiring reflex-level responses.
Future Work
- Incorporate uncertainty modeling by representing object poses as probabilistic distributions within the DEWM.
- Extend the system to handle open-vocabulary scenarios, relaxing the current semi-closed assumption on object categories.
- Fuse force-torque and acoustic signals into the constraint state ($CS$) to enable finer-grained failure diagnosis.
In summary, VLM-DEWM offers a principled path towards deliberative autonomy, transforming reactive vision-language intelligence into a persistent, interpretable, and resilient cognitive agent for dynamic manufacturing environments.