Story
RPT-SR: Regional Prior attention Transformer for infrared image Super-Resolution
Key takeaway
A new AI model can improve the quality of low-resolution infrared images used in surveillance and self-driving cars, which could lead to better object detection and tracking.
Quick Explainer
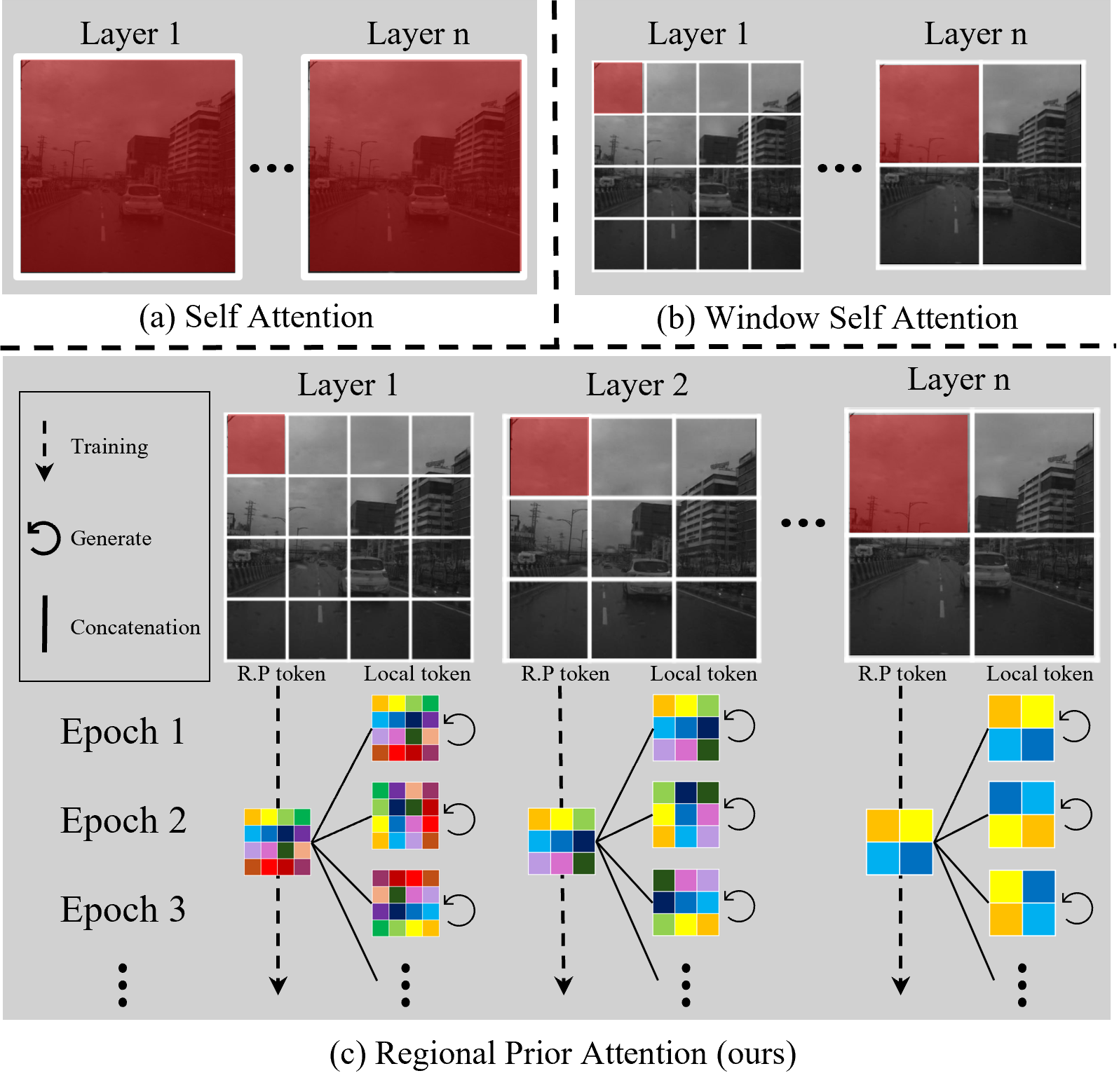
The key innovation in RPT-SR is a Regional Prior Attention (RPA) mechanism that explicitly models the stable spatial layout inherent in fixed-viewpoint infrared imaging scenarios. RPT-SR uses a dual-token framework, fusing a learnable "Regional Prior" token capturing the scene's structural layout with a dynamic "Local" token from the current input frame. This allows the model to efficiently guide the reconstruction of local details, overcoming the "structural amnesia" of prior super-resolution methods. By injecting these spatial priors into the attention process, RPT-SR can focus its capacity on recovering salient local content rather than repeatedly rediscovering redundant global structure.
Deep Dive
Technical Deep Dive: RPT-SR: Regional Prior attention Transformer for infrared image Super-Resolution
Overview
The work proposes RPT-SR, a novel deep learning architecture for super-resolving infrared (IR) images. The key innovation is a Regional Prior Attention (RPA) mechanism that explicitly encodes the stable spatial layout priors inherent in fixed-viewpoint IR imaging scenarios like surveillance and autonomous driving.
RPT-SR uses a dual-token framework that fuses:
- A learnable, static "Regional Prior" token that captures the scene's invariant spatial structure
- A dynamic "Local" token generated from each input frame to model its unique content
By injecting these regional priors into the attention process, the model can efficiently guide the reconstruction of local details, escaping the "structural amnesia" of prior super-resolution methods.
Problem & Context
- Infrared imaging (LWIR and SWIR) is critical for robust, all-weather perception in applications like autonomous driving and surveillance
- However, IR sensors have fundamental limitations in resolution due to physical and economic constraints
- Super-resolution is a key solution to overcome these hardware limitations
- Existing CNN and Transformer-based SR models do not explicitly model the strong spatial priors inherent in fixed-viewpoint IR scenes
- This leads to inefficient, redundant learning as the models relearn the same layout regularities in every frame
Methodology
- RPT-SR uses a deep transformer-based backbone with a novel Regional Prior Attention (RPA) module
- RPA fuses a learnable, static "Regional Prior" token capturing the scene's structural layout with a dynamic "Local" token from the current input
- These tokens are processed by a Hierarchical Attention mechanism that allows the global priors to modulate the reconstruction of local details
- The Regional Prior tokens are optimized end-to-end along with the main pixel reconstruction loss, accelerating their learning
Data & Experimental Setup
- Evaluated on both Long-Wave Infrared (LWIR) and Short-Wave Infrared (SWIR) super-resolution tasks
- LWIR datasets: M3FD, TNO
- SWIR dataset: RASMD
- $\times$4 and $\times$2 upscaling factors
- Compared to recent state-of-the-art CNN and Transformer-based SR methods
Results
- Achieves new state-of-the-art perceptual quality on the M3FD LWIR dataset, as measured by LPIPS, MUSIQ, and MANIQA
- Maintains strong performance on TNO and RASMD, demonstrating versatility across IR modalities
- Outperforms prior methods in both $\times$4 and $\times$2 super-resolution tasks
- Qualitative results show RPT-SR excels at preserving fine details and textures compared to competing approaches
Interpretation
- The proposed Regional Prior Attention mechanism effectively encodes the stable spatial layout priors inherent in fixed-viewpoint IR scenes
- This allows the model to focus its attention and capacity on reconstructing salient local content, rather than repeatedly rediscovering redundant global structure
- The dual-token design of fusing learnable priors with dynamic input features provides a favorable balance between efficiency and perceptual quality
Limitations & Uncertainties
- The work does not explore compressing or distilling the Regional Prior tokens to further reduce model size
- Extending the regional prior concept to other restoration tasks like video super-resolution is left for future work
What Comes Next
- Investigate techniques to compress the Regional Prior tokens, enabling more efficient deployment
- Explore applying the Regional Prior idea to other vision tasks beyond super-resolution, like video enhancement, denoising, or restoration