Story
Earth AI: Unlocking Geospatial Insights with Foundation Models and Cross-Modal Reasoning
Key takeaway
Foundation models and cross-modal AI can unlock new insights from vast satellite and geospatial data, helping us better understand and monitor our planet.
Quick Explainer
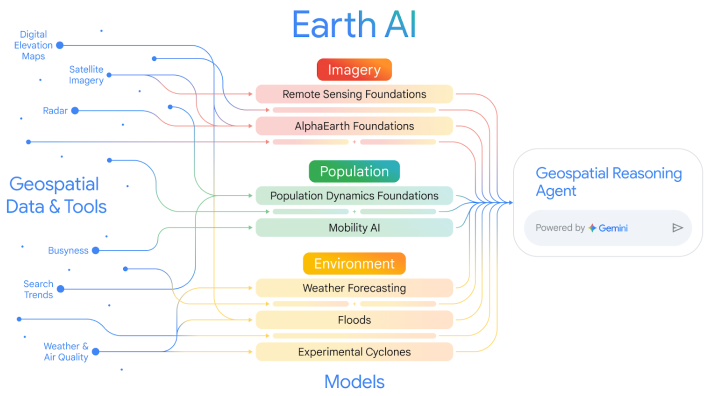
Earth AI leverages advanced foundation models and cross-modal reasoning to unlock powerful geospatial insights. Remote sensing models analyze imagery to detect objects, while population dynamics models capture regional human behavior patterns. These are combined with environmental models tracking natural processes like weather and disasters. An intelligent agent orchestrates these components, bridging raw data and actionable understanding. This integrated, multi-modal approach enables Earth AI to tackle complex, multi-step queries, significantly outperforming prior systems and lowering the barrier for non-experts to leverage sophisticated geospatial intelligence.
Deep Dive
Technical Deep Dive: Earth AI: Unlocking Geospatial Insights with Foundation Models and Cross-Modal Reasoning
Overview
This paper introduces Earth AI, a comprehensive system that leverages foundation models and cross-modal reasoning to enable significant advances in our ability to unlock novel and profound insights into our planet. The key components are:
- Remote Sensing Foundation Models: State-of-the-art vision-language models, open-vocabulary object detectors, and pre-trained vision backbones that provide flexible, high-performance capabilities for analyzing satellite, aerial, and ground-level imagery.
- Population Dynamics Foundation: A model that fuses diverse datasets to capture the dynamics of human behavior and its geographic context, providing compact regional embeddings with global coverage and temporal evolution.
- Environmental Models: Specialized models and APIs for weather forecasting, flood prediction, and cyclone tracking that provide dynamic insights into the Earth's natural processes.
- Geospatial Reasoning Agent: An intelligent agent that orchestrates these diverse models and datasets to answer complex, multi-step queries, bridging the gap between raw geospatial data and actionable understanding.
Key Findings
Remote Sensing Foundation Models
- Vision-Language Models: Achieved state-of-the-art zero-shot classification performance on standard remote sensing benchmarks.
- Open-Vocabulary Object Detection: Our remote sensing variant of OWL-ViT outperformed the baseline by a large margin in both zero-shot and few-shot regimes.
- Pre-trained Backbone: Our multi-task pre-trained vision backbone demonstrated superior performance across a wide range of downstream tasks compared to other leading models.
Population Dynamics Foundation
- Global Embeddings: Expanded the model's spatial coverage to 17 countries, enabling consistent analysis across borders.
- Temporal Embeddings: Created monthly embeddings spanning the last 2 years, improving the model's ability to capture dynamic human behavior patterns.
- Independent Validation: The model's embeddings have been extensively validated by external partners across various real-world applications, confirming their practical utility.
Combining Earth AI Models
- FEMA Risk Scores: Combining Population Dynamics and AlphaEarth Foundations yielded an 11% relative increase in R^2 when predicting 20 FEMA risk indices compared to using either model alone.
- Health Statistics: Integrating both embeddings improved R^2 by 7% over Population Dynamics alone and 43% over AlphaEarth alone when predicting 21 CDC health indicators.
- Disaster Relief: Bellwether's hurricane damage prediction model, which combines Google's cyclone forecasts, building data, and Population Dynamics Foundations, achieved an error of only 3% compared to the observed number of damaged buildings 3 days before Hurricane Ian's landfall.
Geospatial Reasoning Agent
- Fact-finding and Analytics: The Geospatial Reasoning Agent outperformed baseline Gemini agents by 37% on descriptive/retrieval tasks and 124% on analytical/relational tasks.
- Crisis Response: On a benchmark of 10 complex crisis scenarios, the agent achieved an average Likert score of 0.87, significantly outperforming the baseline Gemini 2.5 Pro agent's average of 0.38.
Limitations and Future Work
- Remote Sensing Models: Currently focused on high-resolution RGB imagery, future work will expand to temporal tasks and a broader range of sensor modalities.
- Population Dynamics: Plans to extend the temporal range, increase geographic/temporal granularity, and better handle real-world data gaps.
- Model Integration: Develop a unified meta-Earth model to create a shared, multi-modal representation of the planet, addressing challenges in aligning models at different spatial and temporal scales.
- Geospatial Reasoning: Expand the agent's domain coverage, enhance robustness to out-of-distribution queries, and develop a more comprehensive evaluation framework with human expert review.
Conclusion
This work demonstrates that the future of geospatial AI lies in integrated, multi-modal ecosystems orchestrated by advanced AI reasoning engines. By combining specialized foundation models across Imagery, Population, and Environment domains, Earth AI unlocks unprecedented predictive power and actionable insights for a wide range of real-world applications, from disaster response to public health. The agentic reasoning layer further lowers the barrier to entry, enabling even non-expert users to leverage this sophisticated geospatial intelligence.