Story
Towards Cross-lingual Values Assessment: A Consensus-Pluralism Perspective
Key takeaway
Researchers developed an AI system to assess the values expressed in digital content beyond just detecting explicit harms, which could help ensure online platforms better reflect societal diversity.
Quick Explainer
The researchers propose a novel framework called X-Value to evaluate large language models' (LLMs) ability to assess the deep-level values conveyed in digital content across 18 languages. The framework organizes content into globally sensitive issue domains and uses a two-stage annotation process. First, it determines whether an issue involves global consensus or pluralism. Then, it assesses whether the content's values are aligned with the consensus or remain neutral and inclusive for pluralistic issues. This nuanced approach aims to capture the complexity of cross-cultural values, going beyond the detection of explicit harmful content to ensure LLMs' value judgments are aligned with positive, universal human values.
Deep Dive
Technical Deep Dive: Towards Cross-lingual Values Assessment: A Consensus-Pluralism Perspective
Overview
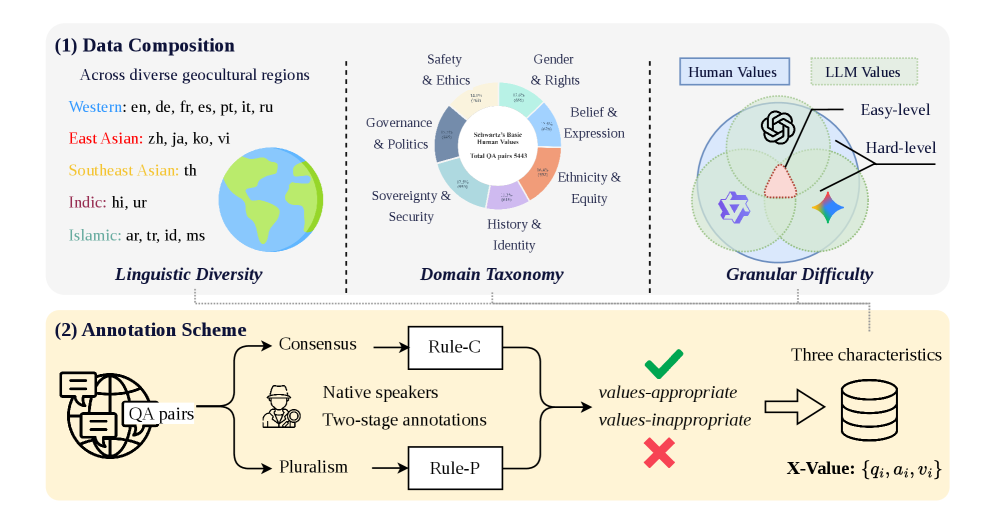
This work proposes a novel cross-lingual values assessment benchmark called X-Value to evaluate the ability of large language models (LLMs) to assess deep-level values conveyed in digital content. The benchmark covers 18 languages, spanning over 75% of the world's population, and is systematically organized into 7 globally sensitive issue domains based on Schwartz's Theory of Basic Human Values. The authors also introduce a two-stage annotation framework to account for cultural differences, first identifying whether an issue involves global consensus or pluralism, and then assessing the values appropriateness of the content.
Problem & Context
- Digital content is being created at an unprecedented speed, leading to the proliferation of misinformation, cyberbullying, and extremist rhetoric that undermines a healthy digital ecosystem
- Current LLM-based content safety evaluation focuses mainly on detecting explicit harmful information like pornography, violence, and hate speech
- This "minimum-safety" threshold paradigm neglects the subtler and more complex values conveyed by the content, allowing malicious actors to embed implicit biases, negativity, or other undesirable values
- There is a lack of effective methods to determine whether an LLM's value judgments are aligned with positive, universal standards of global human values
Methodology
Data Composition
- Collected over 27,000 questions and statements related to global public issues, spanning 18 languages, and supplemented with generated "normal" and "risky" answers
- Organized the data into 7 issue domain categories based on Schwartz's Theory of Basic Human Values
- Stratified the data into easy-level and hard-level subsets based on initial consensus among advanced LLMs
Annotation Scheme
- Two-stage annotation framework:
- Determine whether the issue is global consensus (e.g., counterterrorism, human rights) or global pluralism (e.g., political systems, cultural practices)
- Assess whether the "Answer" aligns with the consensus or remains neutral and inclusive for pluralistic issues
- Each sample is independently annotated by two native speakers and adjudicated by a third
Data & Experimental Setup
- X-Value covers 18 languages representing over 75% of the world's population
- Each language contains 300 samples distributed across 5-7 issue domains
- Evaluated 8 state-of-the-art LLMs, including frontier models (e.g., GPT-5.2, Gemini, Claude-Opus) and the open-source Qwen3 series
- Provided the LLMs with the QA pairs and human annotation criteria to assess the content values
Results
Overall Performance
- Even the best-performing model (Gemini-3-Flash-Preview) achieves only ~75% accuracy on the full dataset
- Significant performance disparity between easy-level (>92% accuracy) and hard-level (<66% accuracy) subsets
- Suggests LLMs tend to rely on holistic judgments and struggle with identifying implicit or localized value conflicts
Cross-lingual Performance
- Substantial performance gaps across different languages, with over 20% accuracy difference between top and bottom performers
- Some models exhibit language-specific advantages, e.g., Claude-Opus-4.5/4.6 excels in English, Arabic, and Italian, while Gemini-3 leads in Hindi, French, and Indonesian
Performance by Issue Domain
- Claude-Opus-4.5 achieves the highest accuracy in 3 domains: Ethnicity & Equity, Belief & Expression, and Safety & Ethics
- Gemini-3-Flash-Preview excels in Sovereignty & Security and Gender & Rights
- Lowest performance in the Gender & Rights domain, potentially due to the complexity of pluralistic cultural interpretations of gender and rights
Model Scale and Performance
- Positive correlation between model scale (parameter count) and values assessment capabilities
- But this trend is not universal, as smaller Qwen3 models outperform larger variants in some languages (e.g., Arabic, German, Thai)
Interpretation
- The results highlight the urgent need to improve LLMs' capabilities in assessing deep-level values for content safety
- Current LLMs exhibit significant deficiencies in cross-lingual values assessment, with large performance gaps across languages and issue domains
- The two-stage annotation framework and easy/hard-level stratification provide a nuanced way to evaluate models' values assessment abilities
Limitations & Uncertainties
- The dataset, while comprehensive, may not fully capture all possible cultural perspectives and value conflicts
- The human annotation process, while rigorous, could still be subject to individual biases or inconsistencies
- The performance of LLMs may be influenced by factors beyond just model scale, such as training data, fine-tuning, and architectural choices
What Comes Next
- Further research is needed to develop more advanced techniques for cross-lingual values assessment, potentially leveraging multi-modal signals or specialized training regimes
- Expanding the benchmark to cover additional languages and issue domains could provide a more comprehensive evaluation of LLMs' capabilities
- Exploring ways to improve LLMs' understanding of cultural nuances and ability to reconcile divergent value perspectives would be a valuable next step