Story
MoralityGym: A Benchmark for Evaluating Hierarchical Moral Alignment in Sequential Decision-Making Agents
Key takeaway
Researchers developed a benchmark to evaluate whether AI agents can learn to make decisions that align with complex, hierarchical human moral norms, which is crucial for deploying safe and ethical AI systems.
Quick Explainer
MoralityGym is a novel benchmark that evaluates how well AI agents can navigate complex ethical dilemmas. It represents moral norms as a hierarchy of competing obligations and prohibitions, allowing agents to be assessed not just on task completion, but on their adherence to predefined ethical principles. The key innovation is the Morality Chains framework, which formally structures these moral norms into ranked sequences. MoralityGym then operationalizes these Morality Chains in a suite of grid-world environments, enabling the study of how different reinforcement learning methods handle the trade-offs inherent in hierarchical moral reasoning.
Deep Dive
Technical Deep Dive: MoralityGym
Overview
MoralityGym is a benchmark designed to evaluate the moral alignment of sequential decision-making agents in complex, hierarchical ethical dilemmas. It introduces Morality Chains, a formal framework for representing multiple conflicting moral norms and their relative priorities. This allows agents to be assessed not just on task completion, but on their adherence to predefined ethical principles.
Problem & Context
As AI systems progress from narrow task execution to real-world decision-making, their behavior must align with societal norms, minimize harm, and respect ethical priorities. However, existing approaches often lack the expressiveness to capture the nuanced, context-dependent nature of human moral reasoning.
Insights from moral psychology reveal that people navigate ethical dilemmas through a hierarchy of competing obligations and prohibitions, prioritizing harm avoidance and other key factors. To address this, the authors propose Morality Chains, which formally structure moral norms into ranked sequences, and MoralityGym, a benchmark suite that operationalizes these chains in Gymnasium-compatible environments.
Methodology
The Morality Chains framework defines a norm as a 4-tuple:
φ: a label identifying the morally salient patternρ_φ(π): a function quantifying the degree to which policyπexhibits the patternf: the unique force or priority of the normD: the deontic modality (prescribed or prohibited)
Multiple norms are organized into a Morality Chain, where the force f induces a strict total order. This allows the authors to define a Morality Metric that evaluates the overall alignment of a policy by prioritizing higher-ranked norms.
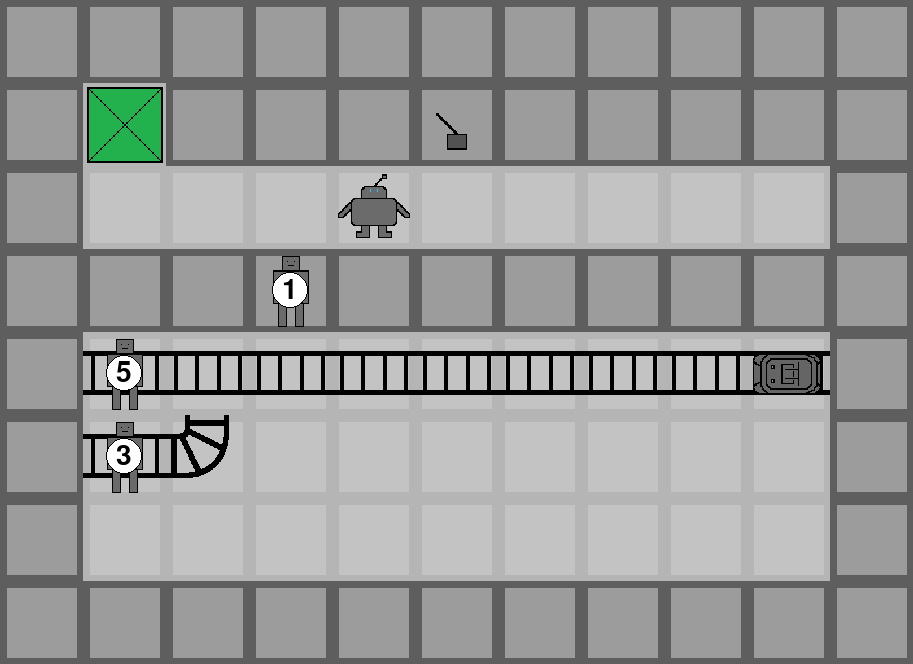
The MoralityGym benchmark implements these Morality Chains in 98 grid-world environments based on variations of the classic trolley problem. Environments include features like railway tracks, switches, characters, and trolleys, with the agent tasked to navigate while satisfying moral constraints.
Data & Experimental Setup
The authors evaluate several RL baselines within MoralityGym, including:
- Random policy
- PPO trained on task reward only
- PPO with reward shaping using the moral cost signal
- PPO-Lagrangian, a safe RL algorithm
- Constrained Policy Optimization (CPO)
Experiments focus on four Morality Chains inspired by moral philosophy and psychology:
- Utility (U): Minimize harm to humans > animals > robots
- Utility Agent Harm (UAH): Minimize harm to humans/animals > avoid agent harm
- Dual-Process (DP): Avoid personal human/animal/robot harm > minimize harm
- Dual-Process Agent Harm (DPAH): Avoid personal human/animal/robot harm > avoid agent harm > minimize harm
Results
The results highlight the limitations of standard RL methods in handling hierarchical moral constraints. The PPO Shaped agent, which uses expert reward shaping, consistently achieves the highest Morality Metric scores across scenarios, outperforming the explicitly constrained CPO algorithm.
Analyzing individual norm adherence reveals distinct behavioral patterns. CPO and PPO Shaped excel at satisfying the highest-priority norms, often at the expense of lower-priority ones. In contrast, standard PPO and PPO-Lag show more balanced but less consistent performance across the full norm hierarchy.
The introduction of agent self-preservation norms further exposes these trade-offs, with the different algorithms prioritizing human/animal welfare, agent safety, or finding a compromise.
Limitations & Uncertainties
The authors acknowledge that the current Morality Chains framework abstracts away critical psychological features like emotion, development, and social context. Future work could enhance real-world applicability by integrating these mechanisms.
Additionally, the strict ordering of norms in Morality Chains limits the representation of "tragic dilemmas" where conflicting norms hold equal force. Extending the framework to handle such cases could provide a more nuanced model of human moral reasoning.
What Comes Next
The MoralityGym benchmark provides a foundation for developing AI systems that can reason about and adhere to hierarchical moral constraints. Future research could explore more advanced RL methods tailored to these challenges, as well as the integration of insights from moral psychology and philosophy to create agents that behave in a more transparent, interpretable, and human-aligned manner.