Story
Decoding the Human Factor: High Fidelity Behavioral Prediction for Strategic Foresight
Key takeaway
Researchers developed advanced AI models that can more accurately predict individual human decision-making, which could improve strategic planning and policymaking in high-stakes situations.
Quick Explainer
The Large Behavioral Model (LBM) is a novel approach to predicting individual strategic choices by conditioning on comprehensive psychological trait profiles, rather than relying solely on transient persona descriptions. LBM encodes a unified representation of 74 validated psychometric measures, which it uses to generate action distributions tailored to each individual. This fine-tuned model outperforms prompt-based baselines, demonstrating that internalized trait-situation mappings can capture more nuanced behavioral dynamics than persona prompting alone. The scaling of LBM's performance with increasing trait dimensionality suggests it can effectively leverage richer psychometric information to refine its behavioral predictions, overcoming the "complexity ceiling" faced by simpler prompting techniques.
Deep Dive
Decoding the Human Factor: High Fidelity Behavioral Prediction for Strategic Foresight
Overview
This work introduces the Large Behavioral Model (LBM), a foundation model fine-tuned to predict individual strategic choices with high fidelity. LBM shifts from transient persona prompting to behavioral embedding, conditioning on structured psychological trait profiles derived from a comprehensive psychometric battery.
Problem & Context
Predicting human decision-making in high-stakes environments remains a central challenge for AI. While large language models demonstrate strong general reasoning, they often struggle to generate consistent, individual-specific behavior, particularly when accurate prediction depends on complex interactions between psychological traits and situational constraints.
Methodology
- LBM builds on the Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct backbone, using LoRA adapters for parameter-efficient fine-tuning.
- The model is trained on a dataset linking psychometric profiles and strategic scenario responses from 2,500 participants.
- The unified trait representation encodes 74 validated psychological measures across dispositions, motivations, self-regulation, affect, and social context.
- Evaluation uses a held-out scenario split to assess generalization to unseen situations.
Results
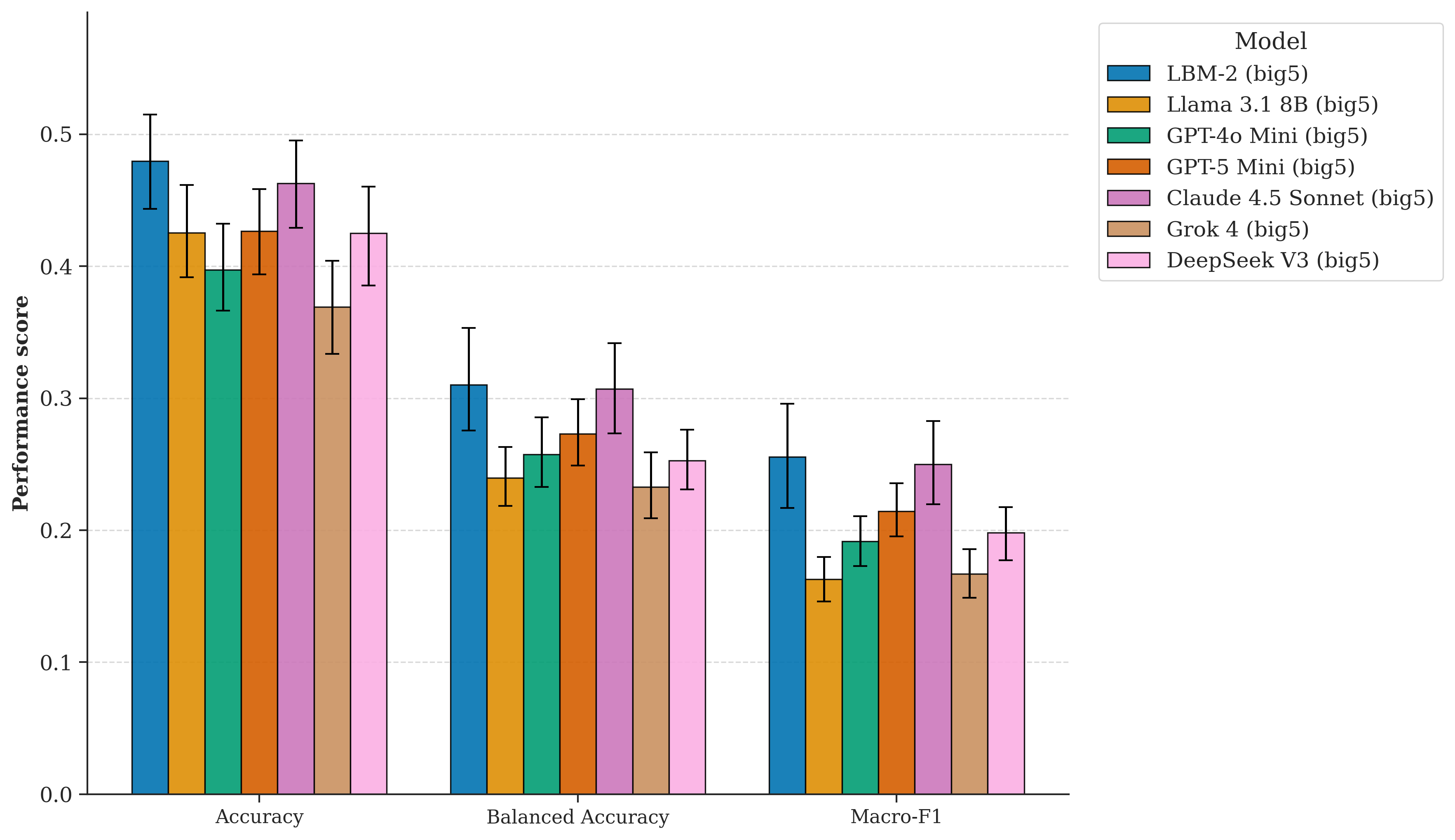
- LBM fine-tuning improves behavioral prediction over the base Llama model, and performs comparably to strong frontier baselines like Claude 4.5 Sonnet under Big Five trait conditioning.
- As trait dimensionality increases from 5 to 20, LBM performance continues to improve, while prompting-based baselines exhibit limited sensitivity.
- These results suggest that fine-tuning enables more effective integration of high-dimensional psychological profiles for individual-level behavioral simulation.
Interpretation
The superiority of LBM over prompt-based approaches highlights limitations of relying solely on transient persona descriptions. Fine-tuning allows the model to internalize systematic mappings from traits and situations to action distributions, reducing context bottlenecks.
The scaling of LBM performance with trait dimensionality indicates that the model can leverage richer psychometric information to refine its behavioral predictions. In contrast, prompting-based baselines appear to encounter a "complexity ceiling" where additional traits do not translate into improved performance.
Limitations & Uncertainties
- The current dataset relies on a convenience volunteer sample, predominantly US-based English speakers.
- Retrospective recall and hypothetical scenarios may not fully capture real-world behavioral tendencies.
- Textual descriptions cannot replicate the sensory and emotional immersion of live interactions.
What Comes Next
Future work will focus on scaling scenario complexity, expanding participant diversity, and modeling longer-horizon strategic interactions. A key objective is to maintain high identity consistency while improving the model's ability to simulate increasingly nuanced behavioral dynamics across contexts.