Story
Agentic Wireless Communication for 6G: Intent-Aware and Continuously Evolving Physical-Layer Intelligence
Key takeaway
The 6G wireless systems are becoming more intelligent and responsive to user needs, moving away from rigid rules towards more autonomous and adaptive control. This could lead to improved performance and reliability for 6G services.
Quick Explainer
The core idea is to enable 6G wireless systems that can autonomously adapt physical-layer link configurations to diverse user preferences and channel conditions. This is achieved through an "agentic AI" architecture called AgenCom, which jointly observes the channel state and user intent expressed in natural language. AgenCom's policy network, centered around large language models, reasons over this multimodal perception to generate a coherent sequence of physical-layer sub-actions. The key novelty is the ability to directly translate user-centric intents, such as reliability or throughput, into executable wireless link decisions, enabled by the integration of domain-adaptive AI and structured action modeling.
Deep Dive
Technical Deep Dive: Agentic Wireless Communication for 6G
Overview
This paper presents an overview of how agentic AI can enable intent-driven, autonomous, and sustainable 6G wireless communications. The key contributions are:
- Reviewing representative 6G physical-layer tasks and the limitations of existing approaches in supporting intent awareness and autonomous operation
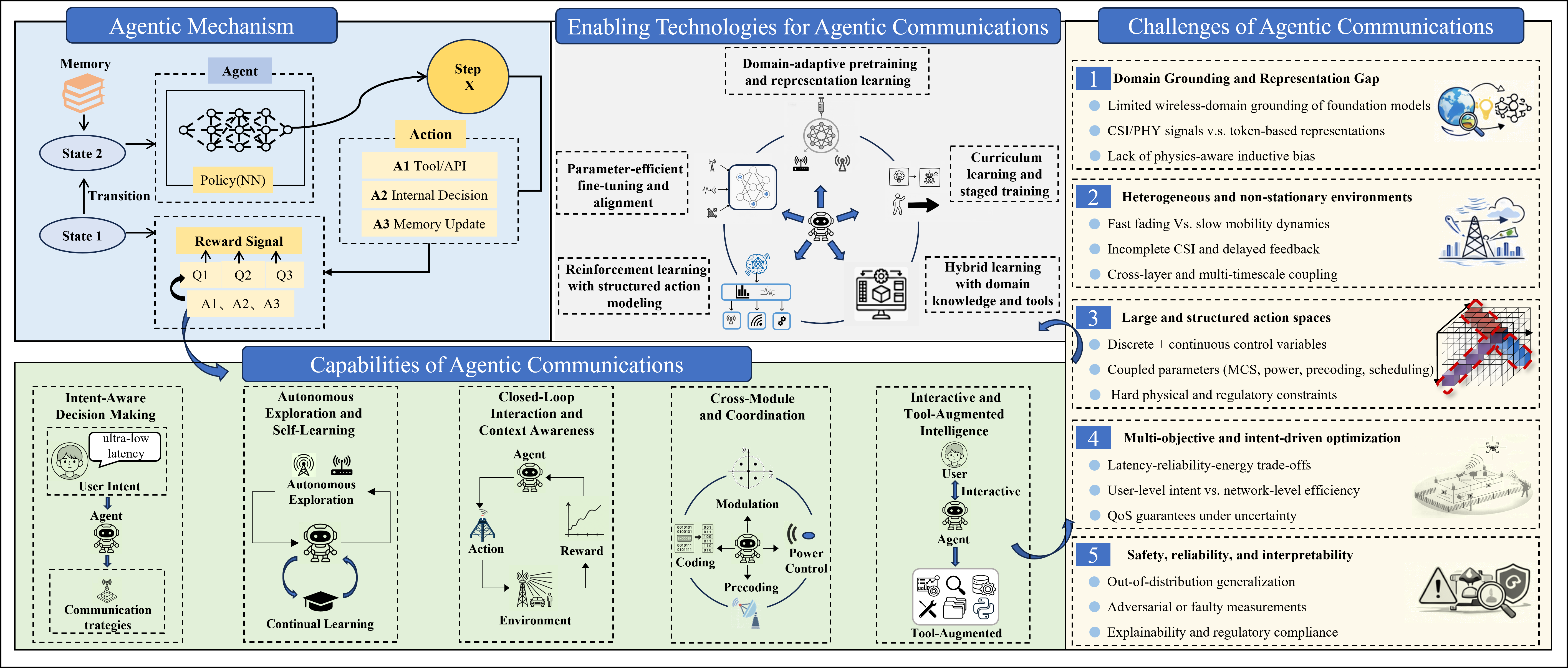
- Proposing agentic AI as a foundational paradigm for 6G wireless systems, and highlighting its key capabilities including intent-aware decision making, autonomous exploration, closed-loop interaction, and cross-module coordination
- Discussing the challenges and enabling technologies for deploying agentic AI in wireless communications, including domain-adaptive pretraining, structured action modeling, and hybrid learning with domain knowledge
- Introducing the AgenCom architecture, an intent-aware communication agent that can dynamically adapt physical-layer link configurations to diverse user preferences and channel conditions
Methodology
Intent-Aware Perception and Representation
- AgenCom jointly observes channel state information (CSI) and user intent expressed in natural language
- This multimodal perception allows associating physical-layer states with semantic intent, enabling user-centric link decisions
LLM-Based Domain-Adaptive Policy Network
- AgenCom's policy network is centered around large language models (LLMs) for reasoning over intent and context
- A lightweight domain adapter injects physical-layer priors to improve controllability and executability
Structured Action Generation
- AgenCom generates a complete link construction strategy by selecting a coherent set of physical-layer configurations
- Link decisions are structured as a sequence of interrelated sub-actions to maintain scalability
Learning-Based Adaptation and Interaction
- AgenCom invokes a physical-layer tool executor to evaluate candidate link configurations under the current environment
- The returned performance metrics are used as reward signals for learning and policy refinement
- A memory module stores historical high-quality samples to improve adaptation speed and decision consistency
Results and Interpretation
Comparison of Output Strategies for Different User Intents
- Under a reliability-oriented intent, AgenCom selects more conservative and robust physical-layer configurations, prioritizing low bit error rate (BER) over throughput
- With a throughput-oriented intent, AgenCom chooses more aggressive modulation and coding to maximize data rate, at the cost of higher BER
- The energy-aware intent leads AgenCom to reduce power consumption by adopting more conservative link configurations, while maintaining reasonable BER and throughput
User Interaction Example
- AgenCom receives the user's intent (e.g., high-throughput) and current channel state information (CSI)
- It then outputs the corresponding communication link decision, demonstrating its ability to translate user preferences into executable physical-layer strategies
Limitations and Uncertainties
The paper acknowledges several key challenges in applying agentic AI to wireless communications:
- Knowledge-domain mismatch between general-purpose AI models and specialized wireless concepts
- Handling heterogeneous and non-stationary wireless environments
- Scaling with large and structured action spaces
- Addressing multi-objective and intent-driven optimization requirements
- Ensuring safety, reliability, and interpretability for operational wireless networks
What Comes Next
To realize agentic AI at scale for 6G, the authors highlight the need for further research in areas such as:
- Domain-adaptive pretraining and representation learning
- Parameter-efficient fine-tuning and alignment techniques
- Reinforcement learning with structured action modeling
- Hybrid learning that integrates domain knowledge and external tools
- Curriculum learning and staged training approaches
Addressing these challenges will be crucial to translate the potential of intent-aware agents into practical, reliable, and sustainable 6G network deployments.