Story
Enhancing Large Language Models (LLMs) for Telecom using Dynamic Knowledge Graphs and Explainable Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Key takeaway
Researchers developed new ways to make AI language models more useful for telecom companies, by improving the models' understanding of industry-specific knowledge and making their outputs more explainable.
Quick Explainer
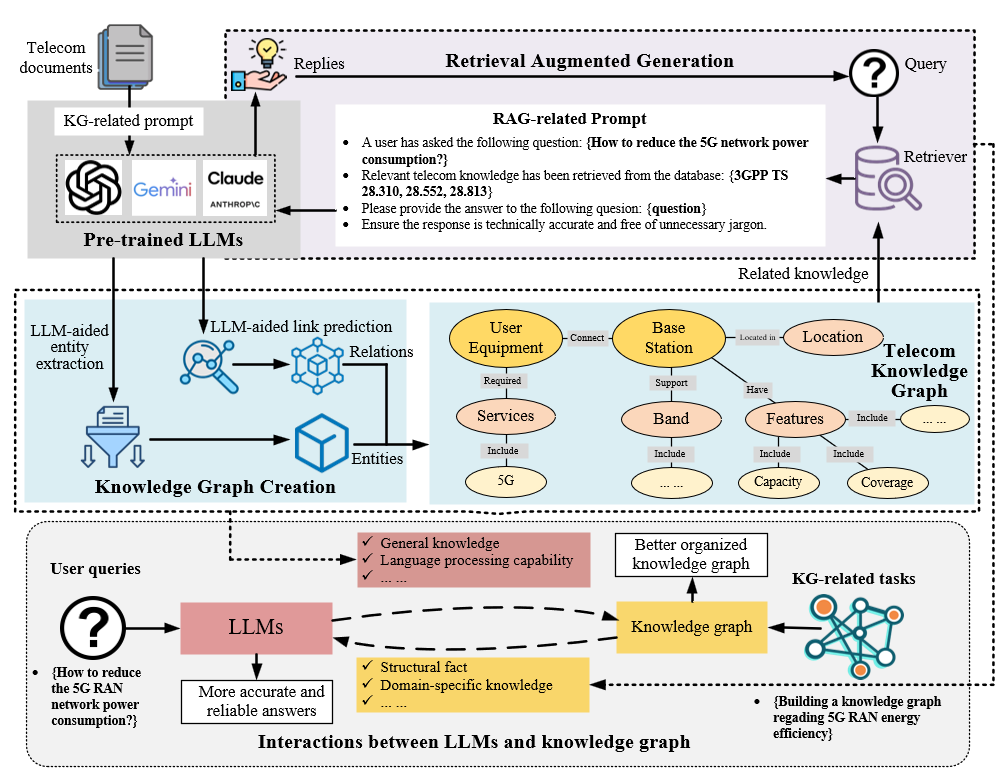
The core idea of KG-RAG is to enhance large language models (LLMs) for telecom tasks by integrating them with a structured knowledge graph (KG). The KG is constructed from technical standards and specifications using entity extraction and link prediction. During inference, the system retrieves relevant, schema-aligned facts from the KG and uses them to ground the LLM's responses, improving accuracy and reducing hallucinations. This retrieval-augmented generation approach also allows the system to provide explainable outputs by verbalizing the retrieved KG triples. The dynamic nature of the KG enables the system to stay up-to-date with rapidly changing telecom network configurations and standards.
Deep Dive
Technical Deep Dive: Enhancing LLMs for Telecom with Dynamic Knowledge Graphs and Explainable Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Overview
This work introduces KG-RAG, a novel framework that integrates knowledge graphs (KGs) with retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) to enhance large language models (LLMs) for telecom-specific tasks. Key aspects:
- Constructs a structured telecom KG from standards documents and technical sources using LLM-based entity extraction and link prediction
- Leverages the KG to retrieve relevant, schema-aligned facts that ground LLM responses, improving accuracy and reducing hallucinations
- Provides explainable outputs by verbalizing KG triples and augmenting generated text with provenance details
- Supports dynamic KG updates to reflect rapid changes in telecom networks and service configurations
Problem & Context
- General-domain LLMs struggle with telecom tasks due to domain complexity, evolving standards, and specialized terminology
- Existing approaches like fine-tuning and prompt engineering have limitations in flexibility and computational cost
- Integrating LLMs with structured knowledge representation and retrieval can address these challenges
Methodology
KG Construction
- Document ingestion: Continuously process 3GPP, O-RAN, and vendor specifications
- Entity & relation extraction: Hybrid pipeline of rule-based matching and LLM-based NER
- Link prediction: TransE-style model to infer missing edges based on ontology constraints
- Schema & storage: Normalize triples to a telecom ontology, store in a property graph database
KG-RAG Retrieval
- Dual-encoder retriever maps queries and triples to a shared embedding space
- Ontology-aware filtering to focus retrieval on relevant semantic types
- Ranking combines embedding similarity, ontology match, and contextual relevance
Explainable Generation
- Verbalize triples into declarative statements using rule-based templates
- Prepend retrieved facts to prompt, enabling ontology-grounded inference
- Augment outputs with provenance details and brief explanations
Data & Experimental Setup
Evaluated on four telecom datasets:
- SPEC5G, Tspec-LLM, TeleQnA, ORAN-Bench-13K
- Used GPT-4-mini as the foundational LLM
- Compared to baselines: LLM-only, RAG, self-RAG, RAPTOR
Assessed on:
- Text summarization (ROUGE, BLEU, METEOR)
- Question answering accuracy
- Hallucination reduction (unverifiable, outdated, fabricated, off-topic)
- Robustness to difficulty levels
Results
Summarization & QA
- KG-RAG outperforms baselines on summarization and QA metrics across datasets
- Particularly strong on standards-heavy and configuration-focused queries
Hallucination Reduction
- KG-RAG exhibits the lowest rates of unverifiable, outdated, fabricated, and off-topic hallucinations
- Structured, provenance-aware retrieval enables more reliable, standards-compliant responses
Dynamic Updates
- Dynamic KG-RAG improves post-change QA accuracy from 72.1% to 84.0%
- Reduces staleness rate from 37.8% to 11.4%, with sub-15s event-to-answer latency
Efficiency
- One-time KG construction completes in tens of minutes
- Incremental updates finish within seconds
- Per-query latency below 1.8s at 95th percentile
Interpretation
- Integrating LLMs with structured, domain-specific KGs and RAG improves factual accuracy, reduces hallucinations, and enhances explainability in telecom tasks
- Dynamic KG updates enable real-time reasoning on rapidly changing network conditions and configurations
- Structured retrieval and generation based on ontology-aligned triples are key to these improvements, outperforming unstructured text-based approaches
Limitations & Uncertainties
- Evaluation focused on standards, specifications, and configuration-related tasks; performance on other telecom applications not assessed
- Efficiency benchmarks conducted on a fixed hardware setup; scalability to large-scale, production environments not evaluated
- Adaptability of the KG-RAG framework to other domains beyond telecom not explored
What Comes Next
- Explore adaptive retrieval strategies that dynamically adjust the triple selection process based on user intent
- Investigate the integration of KG-RAG with other telecom-specific components, such as network simulation and digital twin models
- Assess the generalizability of the KG-RAG approach to other complex, standards-driven domains beyond telecommunications