Story
SpectralGCD: Spectral Concept Selection and Cross-modal Representation Learning for Generalized Category Discovery
Key takeaway
Researchers developed a new AI algorithm that can automatically discover and categorize unknown types of data, potentially enabling better organization and discovery of digital content. This could lead to improved search, recommendation, and content organization systems.
Quick Explainer
SpectralGCD leverages CLIP's cross-modal representations to train a parametric classifier for Generalized Category Discovery. The key ideas are: 1) Representing images as mixtures over semantic concepts captured by CLIP improves the classifier's ability to generalize to novel categories, compared to using raw image features alone. 2) Automatically selecting the most relevant concepts through Spectral Filtering further enhances the representation's quality without manual annotation. 3) Forward and reverse knowledge distillation from a stronger CLIP teacher preserves the semantic meaning of the cross-modal representation during training. This multimodal approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on diverse benchmark tasks while remaining computationally efficient relative to prior multimodal GCD methods.
Deep Dive
Technical Deep Dive: SpectralGCD for Generalized Category Discovery
Overview
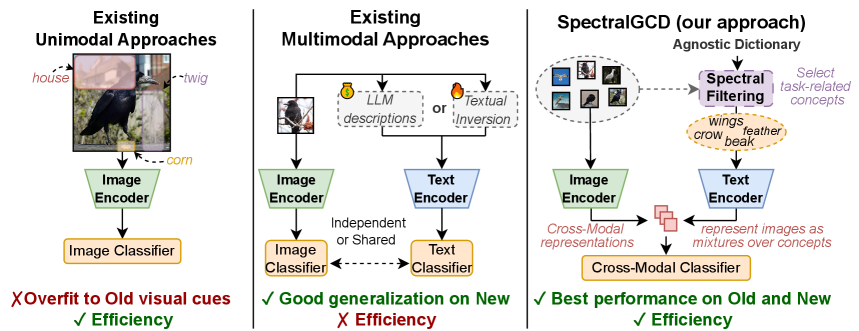
SpectralGCD is a state-of-the-art multimodal approach for Generalized Category Discovery (GCD), a task that aims to identify novel categories in unlabeled data while leveraging a small labeled set of known classes. Key highlights:
- Leverages CLIP's image-text similarities as a unified cross-modal representation to train a parametric classifier, anchoring learning to explicit semantics and reducing overfitting.
- Introduces Spectral Filtering to automatically select task-relevant concepts from a large agnostic dictionary, improving representation quality.
- Employs forward and reverse knowledge distillation to preserve the semantic meaning of the cross-modal representation during training.
- Achieves state-of-the-art performance on 6 benchmark datasets, including fine-grained and coarse-grained classifications, while being more computationally efficient than prior multimodal approaches.
Problem & Context
- GCD aims to cluster unlabeled data containing both known and novel categories, using supervision from a small labeled dataset.
- Existing GCD methods often overfit to scarce labeled data, performing well on known (Old) categories but struggling to generalize to novel (New) ones.
- Multimodal approaches incorporating textual information improve performance, but significantly increase computational cost.
- SpectralGCD addresses these challenges by training a parametric classifier directly on CLIP's cross-modal representations, reducing overfitting while remaining efficient.
Methodology
- Cross-Modal Representation Learning:
- Represent images as mixtures over semantic concepts using CLIP's image-text similarities.
- Train a parametric classifier on this cross-modal representation, which captures class-relevant information more robustly than raw image features.
- Spectral Filtering:
- Automatically select task-relevant concepts from a large agnostic dictionary using an eigendecomposition of the cross-modal covariance matrix.
- The softmax normalization amplifies discriminative concepts while suppressing uninformative ones.
- Knowledge Distillation:
- Use forward and reverse distillation from a frozen CLIP teacher to preserve the semantic quality of the student's cross-modal representation during training.
Data & Experimental Setup
- Evaluated on 6 benchmark datasets: CUB, Stanford Cars, FGVC-Aircraft, CIFAR-10, CIFAR-100, and ImageNet-100.
- Compared to state-of-the-art unimodal and multimodal GCD methods, using clustering accuracy as the evaluation metric.
- Used a CLIP ViT-B/16 as the student image encoder, and a stronger ViT-H/14 as the teacher.
Results
- SpectralGCD consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art on both fine-grained and coarse-grained datasets.
- It achieves significant improvements over existing multimodal approaches, particularly on novel (New) categories.
- SpectralGCD also outperforms the zero-shot performance of its stronger ViT-H/14 teacher model on several benchmarks.
- Training is more efficient than prior multimodal methods, with computation comparable to the unimodal baseline.
Interpretation
- The cross-modal representation learned by SpectralGCD is more discriminative and less prone to overfitting than image features alone.
- Spectral Filtering effectively selects task-relevant concepts, improving representation quality without requiring manual annotation or noisy text generation.
- Knowledge distillation from the teacher helps the student retain semantic meaning in its cross-modal representation during training.
Limitations & Uncertainties
- Performance depends on the choice of teacher model and dictionary used for Spectral Filtering.
- Spectral Filtering may be less robust to significant distribution shifts, although the overall pipeline remains more efficient than alternatives.
- The method still relies on an agnostic dictionary, limiting its ability to handle completely novel concepts not covered by the dictionary.
What Comes Next
- Developing image-specific cross-modal representations to reduce reliance on the teacher and dictionary.
- Exploring techniques to handle more substantial distribution shifts in the unlabeled data over time.
- Investigating methods to automatically expand the dictionary with new concepts as they are encountered.