Story
NL2LOGIC: AST-Guided Translation of Natural Language into First-Order Logic with Large Language Models
Key takeaway
Researchers developed a system that can translate human language into formal logical statements, which could help verify claims against facts in areas like law and policy. This could make it easier to analyze complex documents and ensure decisions are supported by evidence.
Quick Explainer
NL2LOGIC is a framework that translates natural language into formal first-order logic using large language models. Unlike prior work, it takes a structured, top-down approach, incrementally building an abstract syntax tree (AST) that enforces logical grammar. The pipeline consists of a semantic parser that classifies sentences and recursively constructs the AST, followed by an AST-guided generator that produces solver-ready logical expressions. This AST-centric design provides stronger control over the language model's output, improving both syntactic correctness and semantic accuracy compared to prior methods that treat the task as unconstrained text generation.
Deep Dive
NL2LOGIC: AST-Guided Translation of Natural Language into First-Order Logic with Large Language Models
Overview
This paper presents NL2LOGIC, an AST-guided framework for translating natural language into first-order logic using large language models (LLMs). Unlike prior work that treats this task as free-form text generation with limited control, NL2LOGIC incrementally constructs the AST in a top-down manner. This approach provides stronger control over the LLM output, achieving near-perfect syntactic correctness, improving semantic accuracy by 30% on LogicNLI, FOLIO, and ProofWriter datasets, and improving existing neuro-symbolic system Logic-LM by 31% on both syntactic and downstream reasoning task accuracy.
Methodology
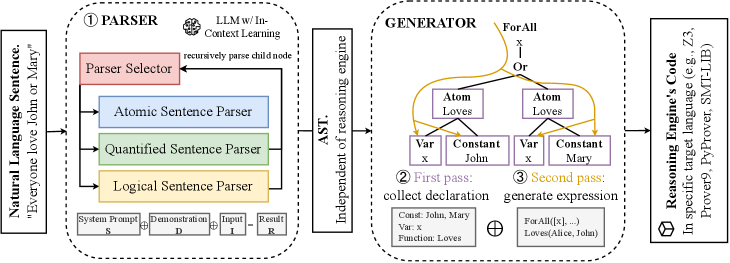
NL2LOGIC adopts a parser-generator architecture designed to ensure syntactic correctness and semantic faithfulness in translating natural language into formal logic. The pipeline consists of two stages:
- Semantic Parser: The semantic parser maps natural language sentences into a first-order logic abstract syntax tree (FOLAST) that strictly enforces logical grammar. It operates recursively through specialized sub-modules to classify each sentence as atomic, quantified, or logical, and then invokes the corresponding sub-parser. This top-down recursion incrementally builds the AST, limiting error propagation and maintaining semantic faithfulness across sentences of varying complexity.
- AST-Guided Generator: The AST-guided generator converts the FOLAST produced by the parser into solver-ready code (e.g., Z3 or SMT-LIB). It follows a two-pass algorithm: the first pass collects all variable, constant, and relation signature declarations to establish a consistent global context, while the second pass revisits each node to emit logical expressions that respect operator precedence, quantifier scope, and relation arity.
Data & Experimental Setup
We evaluate NL2LOGIC on three natural language inference (NLI) datasets: LogicNLI, ProofWriter, and FOLIO. These datasets contain a total of 3,000 premise-hypothesis pairs, where each premise consists of a set of sentences representing logical rules, and the hypothesis is a single sentence expressible as one logical statement.
We compare NL2LOGIC against two baselines:
- Grammar-Constrained Decoding (GCD): A state-of-the-art approach that enforces syntactic correctness by encoding the target formal language as a context-free grammar and constraining the LLM's decoding process.
- Logic-LM: A representative neuro-symbolic framework that translates natural language into first-order logic using few-shot prompting, without explicit syntactic or semantic constraints.
We evaluate using the same 12 LLM models (Gemma, LLaMA, Mistral, and Qwen) ranging from 0.5B to 27B parameters.
Results
RQ1: Syntax Correctness
NL2LOGIC consistently outperforms the GCD baseline, achieving near-perfect syntactic correctness (up to 0.99) across all model families and scales. The improvement is most pronounced in smaller models, demonstrating that the iterative parser effectively mitigates syntax drift.
RQ2: Semantic Correctness
NL2LOGIC improves performance on natural language inference tasks by an average of 31% over the GCD baseline. The iterative AST construction approach lowers the LLM's cognitive load, particularly benefiting smaller models.
RQ3: Integration with Neuro-Symbolic Systems
Integrating NL2LOGIC into the Logic-LM pipeline improved the executable rate from 0.01-0.94 to near-perfect 0.99 across all models and datasets. This syntactic validity improvement translated into a 31% accuracy gain on executable rules, demonstrating the practical value of NL2LOGIC as a modular component in neuro-symbolic systems.
Limitations & Uncertainties
NL2LOGIC currently handles individual sentences in isolation, without considering contextual information from adjacent sentences or the entire text. This limitation affects the translation of sentences that require cross-sentence dependencies, such as co-reference or implicit relational links.
Additionally, NL2LOGIC relies on structured output capabilities available in LLM serving frameworks. Not all platforms support this feature natively, requiring custom integration work.
What Comes Next
Future work should explore techniques to incorporate cross-sentence context into the logical translation process, enabling more comprehensive and semantically coherent FOL representations. Investigating alternative LLM integration approaches that do not rely on structured output would also broaden the applicability of this framework.